북한이 향후 성능 검증을 위해 추가 핵실험을 단행할 수 있다고 미국 국방정보 당국이 진단했습니다. 북한의 핵무기 정책이 억제 중심에서 벗어나고 있다는 점도 지적했습니다. 이조은 기자가 보도합니다.
미 국방부 산하 국방정보국(DIA)은 지난 23일 공개한 보고서에서 북한이 최근 몇 년간 핵무기 프로그램을 지속적으로 강화하고 있다고 밝혔습니다.
[DIA 보고서] “North Korean forces remain active, performing simulation drills to load and launch nuclear weapons to threaten the United States and its allies in the region. North Korea has demonstrated the capability to produce plutonium and highly enriched uranium, and continues to increase the stockpile of these materials to support its nuclear weapons program.”
중국, 러시아, 북한, 이란의 핵무기 프로그램 최신 동향을 담은 보고서는 “북한군은 미국과 역내 동맹국을 위협하기 위해 핵무기를 장착하고 발사하는 모의 훈련을 실시하는 등 여전히 활발히 활동하고 있다”고 밝혔습니다.
또 “북한은 플루토늄과 고농축 우라늄 생산 능력을 입증했으며, 핵무기 프로그램을 지원하기 위해 이런 물질의 비축량을 계속 늘리고 있다”고 지적했습니다.
특히 김정은 북한 국무위원장이 2021년 1월 노동당 8차 대회 보고에서 북한이 “핵무기의 소형화, 경량화, 표준화, 전술화” 능력을 발전시키고 “초대형 수소탄” 개발을 완료했다고 주장한 데 주목했습니다.
[DIA 보고서] “Kim claimed, during a January 2021 update to the Eighth Congress of the Workers Party of Korea, that North Korea advanced its capabilities to “make nuclear weapons miniaturized, light-weight, standardized, and tactical weapons” and completed the development of “super-large hydrogen bombs.” DIA interprets this is a reference to creating smaller diameter, single-stage fission devices and completing the design of its thermonuclear weapon. These new developments may be driving the need for a nuclear test to validate its performance.”
이어 “DIA는 이를 더 작은 직경의 단일 단계 핵분열 장치를 만들고 열핵무기 설계를 완료했다는 의미로 해석하고 있다”고 밝혔습니다.
그러면서 “이런 새로운 개발로 인해 성능을 검증하기 위한 핵실험이 필요할 수 있다”고 평가했습니다.
북한의 탄도미사일 역량 강화 추세에도 주목했습니다.
[DIA 보고서] “In the past 5 years, North Korea has diversified its ballistic missile force to include solid-fueled systems. Solid-propellant missiles offer operational advantages over liquid-fueled systems, eliminating the time required to fuel a missile before firing it… North Korea is committed to developing long-range, nuclear-armed missiles that are capable of posing a direct threat to the U.S.”
보고서는 “지난 5년 동안 북한은 고체 연료 시스템을 포함해 탄도미사일 전력을 다양화했다”며 “고체 추진체 미사일은 발사 전 연료 주입 시간이 필요하지 않아 액체 연료 시스템에 비해 작전상 이점을 제공한다”고 지적했습니다.
또한 “북한은 미국에 직접적인 위협이 될 수 있는 장거리 핵무장 미사일을 개발하는 데 전념하고 있다”고 강조했습니다.
북한의 핵 기술 이전 가능성도 제기했습니다.
“북한은 관계를 은폐 혹은 부인하거나 평화적 민간 핵 프로그램을 지원하는 것이라고 주장할 수 있다고 믿는다면 핵 전문 지식이나 기술을 확산할 의향이 있을 것”이라는 분석입니다.
[DIA 보고서] “Pyongyang probably would be willing to proliferate nuclear expertise or technology if it believed it could keep the relationship covert, deniable, or claim it was supporting a peaceful civilian nuclear program.”
보고서는 북한의 핵무기 정책이 억제 중심에서 벗어나 더욱 능동적이고 전술적인 핵 사용 의도를 보이고 있다고 평가했습니다.
북한이 최신 탄도미사일 시스템을 꾸준히 개발하고 있는 것은 “생존 가능한 핵무기 운반 능력을 개발하고 유지하려는 의도를 보여준다”는 것입니다.
[DIA 보고서] “The steady development of modern ballistic missile systems highlights North Korea’s intention to develop and maintain a survivable nuclear weapon delivery capability. This capability, at the first sign of a U.S. or South Korea strike, suggests potential for usage at any stage of a crisis or conflict...Additionally, regime statements suggest North Korea’s use options and target selection will evolve as its nuclear force grows, potentially lowering its nuclear use threshold in the coming years.”
이어 “이런 역량은 미국이나 한국이 공격할 조짐을 보이면 위기나 분쟁의 모든 단계에서 사용될 수 있다는 점을 시사한다”고 밝혔습니다.
또한 “북한 정권이 내놓은 성명들은 북한의 핵무기 전력 확대에 따라 사용 옵션과 목표물 선정 (기준) 또한 진화해 향후 몇 년 동안 핵 사용 임계치를 낮출 수 있음을 시사한다”고 덧붙였습니다.
보고서는 현재 북한의 전략적 우선순위는 김정은 체제에서 지속적으로 관찰된 몇 가지 흐름에 반영돼 있다며 “북한이 탄도미사일 시험 발사와 훈련을 일상화하고 핵무기를 탑재할 수 있는 운반 시스템의 수와 유형을 확대하며 북한의 핵무기 프로그램과 탄도미사일 간의 연계를 공개적으로 강조하는 것이 그것”이라고 지적했습니다.
[DIA 보고서] “Pyongyang’s current strategic priorities are reflected in several trends observed over the course of Kim Jong Un’s leadership to date. Routinization of ballistic missile flight tests and training launches; Expansion of the numbers and types of nuclear-capable delivery systems; Public emphasis on the linkage between North Korea’s nuclear weapons program and its ballistic missiles.”]
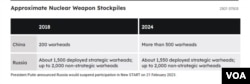
한편 보고서는 중국의 핵무기 프로그램과 관련해 “중국은 2018년에 평가된 초기 성장 추정치를 훨씬 뛰어넘어 현재 500개 이상의 투발 가능한 핵탄두를 보유하고 있다”고 평가했습니다.
이어 “2030년까지 중국은 1천기 이상의 운용 가능한 핵탄두를 보유할 것으로 추정되며, 이 중 대부분은 미국 본토를 사정권에 둘 수 있는 시스템에 배치될 것으로 예상된다”고 밝혔습니다.
[DIA 보고서] “Beijing has far surpassed earlier growth estimates assessed in 2018, and is currently exceeding 500 deliverable nuclear warheads in its stockpile. By 2030, we estimate that China will have more than 1,000 operational nuclear warheads— most of which will be fielded on systems capable of ranging the continental United States… Over the past 4 years, Russia has maintained the largest foreign nuclear stockpile in the world. Moscow maintains about 1,550 deployed strategic nuclear warheads on ICBMs and submarinelaunched ballistic missiles (SLBMs)… Currently, Iran almost certainly does not have nuclear weapons and has agreed not to seek, develop, or acquire nuclear weapons. However, since 2019, Iran has exceeded several of the JCPOA’s limits, including the limits on the quantity and enrichment levels of its uranium stockpile, the locations where Iran enriches uranium, the number and types of enriching centrifuges.”
또 “지난 4년 동안 러시아는 세계에서 가장 많은 해외 핵 비축량을 유지해 왔다”며 “러시아는 대륙간탄도미사일(ICBM)과 잠수함 발사 탄도 미사일(SLBM)에 배치된 약 1천550기를 보유하고 있다”고 평가했습니다.
아울러 “현재 이란은 거의 확실하게 핵무기를 보유하지 않고 있으며 핵무기를 추구, 개발 또는 획득하지 않기로 합의했다”고 밝혔습니다.
그러나 “2019년 이후 이란은 우라늄 비축량과 농축 수준 및 장소, 농축 원심분리기의 수와 유형에 대한 제한을 포함해 포괄적공동행동계획(JCPOA)의 여러 제한을 초과했다”고 지적했습니다.
VOA 뉴스 이조은입니다.








Forum