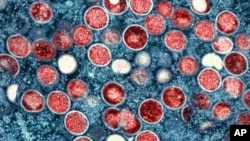
The World Health Organization has renamed monkeypox as mpox, citing concerns the original name of the decades-old animal disease could be construed as discriminatory and racist.
The U.N. health agency said in a statement Monday that mpox was its new preferred name for monkeypox, saying that both monkeypox and mpox would be used for the next year while the old name is phased out.
WHO said it was concerned by the "racist and stigmatizing language" that arose after monkeypox spread to more than 100 countries. It said numerous individuals and countries asked the organization "to propose a way forward to change the name."
In August, WHO began consulting experts about renaming the disease, shortly after the U.N. agency declared monkeypox's spread to be a global emergency.
To date, there have been more than 80,000 cases identified in dozens of countries that had not previously reported the smallpox-related disease. Until May, monkeypox, a disease that is thought to originate in animals, was not known to trigger large outbreaks beyond central and west Africa.
The 10 most affected countries globally are: the United States (29,001), Brazil (9,905), Spain (7,405), France (4,107), Colombia (3,803), Britain (3,720), Germany (3,672), Peru (3,444), Mexico (3,292), and Canada (1,449). They account for 86% of the global number of cases, Agence France-Presse reported.
Outside of Africa, nearly all cases have been in gay, bisexual or other men who have sex with men. Scientists believe monkeypox triggered outbreaks in Western countries after spreading via sex at two raves in Belgium and Spain. Vaccination efforts in rich countries, along with targeted control interventions, have mostly brought the disease under control after it peaked in the summer.
In Africa, the disease mainly affects people in contact with infected animals such as rodents and squirrels. The majority of monkeypox-related deaths have been in Africa, where there have been almost no vaccines available.
U.S. health officials have warned it may be impossible to eliminate the disease there, warning it could be a continuing threat mainly for gay and bisexual men for years to come.
Mpox was first named monkeypox in 1958 when research monkeys in Denmark were observed to have a "pox-like" disease, although they are not thought to be the disease's animal reservoir.
Although WHO has named numerous new diseases shortly after they emerged, including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, or SARS and COVID-19, this appears to be the first time the agency has attempted to rechristen a disease decades after it was first named.
Numerous other diseases, including Japanese encephalitis, German measles, Marburg virus and Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome have been named after geographic regions, which could now be considered prejudicial. WHO has not suggested changing any of those names.