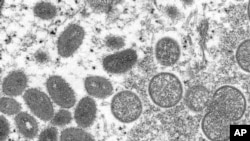
More than 1,600 confirmed monkeypox cases and almost 1,500 suspected cases have been reported this year from seven countries where monkeypox has been detected for years and 32 newly affected countries, according to the World Health Organization director-general, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus.
“Europe remains the epicenter of this escalating outbreak,” Dr. Hans Henri P. Kluge, WHO regional director for Europe, said, with “85% of the global total.”
WHO is convening an emergency meeting next week to discuss the mounting outbreak and whether the name of the disease should be changed.
A group of scientists said in a statement recently on virological.com, “In the context of the current global outbreak, continued reference to, and nomenclature of this virus being African is not only inaccurate but is also discriminatory and stigmatizing. The most obvious manifestation of this is the use of photos of African patients to depict the pox lesions in mainstream media in the global north. Recently, Foreign Press Association, Africa, issued a statement urging the global media to stop using images of African people to highlight the outbreak in Europe.”
Monkeypox, according to a description on WHO’s website, “is a zoonosis: a disease that is transmitted from animals to humans.”
Human-to-human transmission is limited, according to WHO, but can occur “through contact with bodily fluids, lesions on the skin or on internal mucosal surfaces, such as in the mouth or throat, respiratory droplets and contaminated objects.”