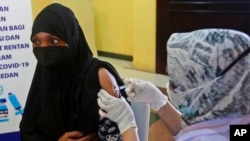
Thousands of refugees in Indonesia are finding themselves shut out of public services including travel and shopping because of a bureaucratic glitch that prevents them from proving they have been vaccinated against COVID-19.
Indonesia is a transit country for 13,175 refugees, more than half of whom are from Afghanistan. Unlike some countries where refugees are kept In camps, refugees in Indonesia can roam freely and use public facilities. Most live around the Jakarta greater metropolitan area.
In 2020, the country launched “Peduli Lindungi,” a digital COVID-19 contact-tracing app giving vaccinated residents access to public facilities and mass transit. The program, however, requires people to upload their 16-digit government-issued civil registry number before they are vaccinated. Only citizens, permanent residents and foreigners with work visas have the number; refugees – more than 56% of whom have been vaccinated -- do not.
The U.N. Refugee Agency, UNHCR, with the support of Indonesian state-owned pharmaceutical company Bio Farma, developed a system to generate a different registration number to allow refugees to register in the app. However, the Jakarta Health Agency, which oversees the public plan, does not have the authority to generate the new numbers. The issue is now under discussion among the Health and Foreign ministries and the UNHCR.
Therefore, the refugees who received their vaccinations at local health clinics under the public vaccination plan did not receive an electronic vaccine certificate that would otherwise be uploaded to the Peduli Lindungi app. They also have no proof of vaccination other than a handwritten slip.
Somali refugee Ahmed Sheikh described the problem he faced when stopped by security guards asking for proof of vaccination at public transportation facilities or shopping malls.
“When we show them a handwritten slip issued by health workers at the public health clinic, they don’t believe it. …. It’s hard to explain to them when they don’t speak English too,” he told VOA.
Dr. Ngabila Salama, the head of the Jakarta Health Agency acknowledged the administrative hurdle, telling VOA the agency is limited by legal uncertainty; it does not have the legal authority to generate a useable civil registration number.
“We need to be accountable for every vaccine that we give out. It’s a shame if we cannot register all the vaccine recipients onto the Peduli Lindungi app. Imagine if we give out over 5,000 vaccines to refugees that are not registered on the Peduli Lindungi app. How can we be accountable for every vaccine, when we must undergo an audit by the Financial Audit Board? They may think we wasted a lot of the vaccines.” she said.
Some refugees are considering postponing getting their first vaccinations or second doses until this administrative problem is solved.
Although Sheikh is already vaccinated, he doubts he will let his wife be vaccinated soon, considering the circumstances.
“I don’t think I’m going to bring my wife to a Puskesmas [local health clinic] to get vaccinated because even if they give her the vaccine, they won’t enable the Peduli Lindungi app for her and can’t give her the electronic vaccine certificate she needs. I don’t want her to get the vaccine if we can’t get an [electronic] vaccine certificate. That’s what all refugees want.”
The UNHCR and nongovernmental organizations are trying to draw attention to the issue.
Zico Pestalozzi, campaign and advocacy coordinator at Suaka, an NGO that handles refugee issues, said “the Refugee Task Force under the Ministry of Political, Security and Legal Affairs should better coordinate [with relevant stakeholders] and ensure inclusive access to the Peduli Lindungi App.
“The UNHCR and NGOs are nongovernmental bodies, so it is up to the government to take charge of this issue and not simply divert responsibility back to the UNHCR,” he said.
Dicky Budiman, an Indonesian epidemiologist at Griffith University in Australia warns that “If we don’t protect this vulnerable population fast enough. We will be keeping a possible ‘pocket of infection.’ It will become a big problem because then it could produce a new variant or at least a new cluster among the refugee community.”
Pestalozzi agreed with Budiman, saying that if this problem lingers, it could turn into a public health risk and set back all the positive initiatives from the Indonesian government to improve refugees’ lives, including providing free vaccines, establishing learning centers and access to vocational learning.