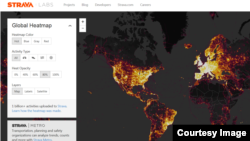
The U.S. military says it is evaluating its policies after a global map of fitness activity drew attention to possible security concerns regarding locations of overseas bases and soldier movements.
Strava published its so-called heat map of user activity in November showing the routes millions of users walked, ran and biked, with the most frequent routes showing up in brighter colors. The company says it excluded activities that users marked as private or ones that took place in areas people did not want to make public.
The activities were tracked using GPS-enabled devices from manufacturers like Fitbit, Garmin and Polar. Even with the exclusions, Strava said its map included 1 billion activities between 2015 and September 2017.
The Washington Post reported on the heat map and its implications, highlighting a Twitter post by Australian student Nathan Ruser who shared the link to the Strava site Saturday.
"It looks very pretty, but not amazing for Op-Sec [operational security]. US Bases are clearly identifiable and mappable," Ruser wrote.
The map shows the most activity in places like the United States, Western Europe, Japan and Brazil. In Iraq, Syria and Afghanistan, activities show up bright against otherwise dark terrain, including in multiple places where the U.S. military is known to have bases or be active.
The wearable devices that transmit the data can be used in several ways, including for example a short run or keeping track of the steps a person takes throughout the day. The result can be lines on the heat map showing loops around the perimeter of a military installation where people exercise or showing where they move from place to place throughout the facility, or elsewhere.
"DoD takes matter like these very seriously and is reviewing the situation to determine if any additional training or guidance is required, and if any additional policy must be developed to ensure the continued safety of DoD personnel at home and abroad," Department of Defense spokeswoman Maj. Audricia Harris said.