Enzymes found in the saliva of wax worms can degrade one of the most common forms of plastic waste, according to research published Tuesday that could open up new ways of dealing with plastic pollution.
Humans produce some 400 million metric tons of plastic waste each year despite international drives to reduce single-use plastics and to increase recycling.
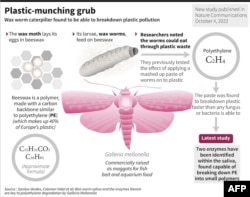
Around a third is polyethylene, a tough plastic thanks to its structure, which traditionally requires heating or radiation before it starts to break down.
There have been several studies showing that microorganisms can release enzymes that start the degradation process on polyethylene, but the process has until now taken months each time.
But the enzymes contained in the saliva of the wax worm moth (Galleria mellonella) can act in only a few hours, Tuesday's research showed.
Researcher Federica Bertocchini, an avid beekeeper, said she originally stumbled on the idea that this small caterpillar had unusual powers when storing honeycombs a few years ago.
"At the end of the season, usually beekeepers put some empty beehives in a storage room, to put them back in the field in the spring," she told AFP.
"One year I did that, and I found my stored honeycombs plagued with wax worms. In fact, that is their habitat."
Bertocchini cleaned the honeycombs and put the worms in a plastic bag.
When she returned a short time later, she found the bag "riddled with holes."
"That raised the question: Is it the result of munching, or is there a chemical modification? We checked that, doing proper lab experiments, and we found that the polyethylene had been oxidized," she said.
In her latest research, Bertocchini, from Madrid's Margarita Salas Centre for Biological Studies (CIB) and her colleagues analyzed proteins in the wax worm saliva and identified two enzymes that could break polyethylene down into small polymers in only a few hours at room temperature.
Writing in the journal Nature Communications they explained how they used another worm's saliva as a control experiment, which produced no degradation compared with the wax worm.
Bertocchini said her team is still trying to figure out precisely how the worms degraded the plastic.
While the study authors stressed that much more research was needed before Tuesday's findings could be implemented at any meaningful scale, there were a number of possible applications.
"We can imagine a scenario where these enzymes are used in an aqueous solution, and liters of this solution is poured over piles of collected plastic in a waste management facility," Bertocchini said.
"We can also imagine small amounts that can reach more remote locations, like villages or small islands, where waste facilities are not available."
She said that further down the line the solution could be used in individual houses, where each family could degrade their own plastic waste.