U.S. stocks are tumbling Friday on worries about whether the U.S. economy can hold up amid the countdown for a cut to interest rates by the Federal Reserve, as a sell-off for stocks whips all the way around the world back to Wall Street.
The S&P 500 was sinking by 2.5% in late morning trading, potentially on pace for its worst day since 2022, and on track for its first back-to-back loss of more than 1% since April. The Dow Jones Industrial Average was down 806 points, or 2%, as of 10:45 a.m. Eastern time, and the Nasdaq composite was 3.1% lower.
A report showing hiring by U.S. employers slowed last month by much more than economists expected sent fear through markets, with both stocks and bond yields dropping sharply. It followed a batch of weaker-than-expected reports on the economy from a day earlier, including a worsening for U.S. manufacturing activity, which has been one of the areas hurt most by high rates.
It was just a couple days ago that U.S. stock indexes jumped to their best day in months after Fed Chair Jerome Powell gave the clearest indication yet that inflation has slowed enough for cuts to rates to begin in September.
Now, worries are rising the Fed kept its main interest rate at a two-decade high for too long in its zeal to stifle inflation. A rate cut would make it easier for U.S. households and companies to borrow money and support the economy, but it could take months to a year for the full effects to filter through.
“The Fed is seizing defeat from the jaws of victory,” said Brian Jacobsen, chief economist at Annex Wealth Management. “Economic momentum has slowed so much that a rate cut in September will be too little and too late. They’ll have to do something bigger than” the traditional cut of a quarter of a percentage point ”to avert a recession.”
Traders are now betting on a roughly two-in-three chance that the Fed will cut its main interest rate by half a percentage point in September, according to data from CME Group. That's even though Powell said on Wednesday that such a deep reduction is “not something we're thinking about right now.”
U.S. stocks had already appeared to be headed for losses before the disappointing jobs report thudded onto Wall Street.
Several big technology companies turned in underwhelming profit reports, which continued a mostly dispiriting run that began last week with results from Tesla and Alphabet.
Amazon fell 11.9% after reporting weaker revenue for the latest quarter than expected. The retail giant also gave a forecast for operating profit for the summer that fell short of analysts’ expectations.
Intel dropped even more, 27.9%, after the chip company’s profit for the latest quarter fell well short of forecasts. It also suspended its dividend payment and said it expects to lose money in the third quarter, when analysts were expecting a profit.
Apple was holding steadier, up 2.4%, after reporting better profit and revenue than expected.
Apple and a handful of other Big Tech stocks known as the “ Magnificent Seven ” have been the main reasons the S&P 500 has set dozens of records this year, in part on a frenzy around artificial-intelligence technology. But their momentum turned last month on worries investors had taken their prices too high and expectations for their profit gains are growing too difficult to meet.
Friday's losses for tech stocks dragged the Nasdaq composite down by more than 10% from its record set in the middle of last month.
Helpfully for Wall Street, other areas of the stock market beaten down by high interest rates had been rebounding at the same time tech stocks were regressing, particularly smaller companies. But they tumbled too Friday on worries that a fragile economy could undercut their profits.
The Russell 2000 index of smaller stocks dropped 4.2%, more than the rest of the market.
In the bond market, Treasury yields fell sharply as traders raised their expectations for how deeply the Federal Reserve would have to cut interest rates. The yield on the 10-year Treasury fell to 3.82% from 3.98% late Thursday and from 4.70% in April.
Amid all the fear, some voices on Wall Street were still advising caution.
“While worries of a policy mistake are rising, one negative miss shouldn’t lead to overreaction,” according to Lara Castleton, U.S. head of portfolio construction and strategy at Janus Henderson Investors.
She points out the U.S. economy is still growing, and inflation is still coming down. The S&P 500, meanwhile, isn’t far off its record set two weeks ago. “Equities selling off should be seen as a normal reaction, especially considering the high valuations in many pockets of the market. It’s a good reminder for investors to focus on the earnings of companies going forward.”
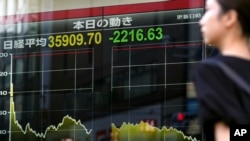
In stock markets abroad, Japan’s Nikkei 225 dropped 5.8%. It's been struggling since the Bank of Japan raised its benchmark interest rate on Wednesday. The hike pushed the value of the Japanese yen higher against the U.S. dollar, potentially hurting profits for exporters and deflating a boom in tourism.
Chinese stocks extended losses this week as investors registered disappointment with the government’s latest efforts to spur growth through various piecemeal measures, instead of hoped-for infusions of broader stimulus, and stock indexes fell across much of Europe.
Commodity prices have also had a rough ridet this week. Oil prices surged after the killings of leaders of Hamas and Hezbollah that fueled fears that a widening conflict in the Middle East could disrupt the flow of crude.
But prices fell back Thursday and Friday on worries that a weakening economy will burn less fuel. A barrel of benchmark U.S. crude tumbled 3.4% Friday to $73.73 and brought its loss for the week to 4.5%.
___