The malaria parasite owes its devastating success to a finely tuned genome that can survive attacks and evade human immune defenses because it retains only the bare essential genes it needs to thrive, scientists have found.
In a detailed study analyzing more than half the genes in the genome of Plasmodium, the parasite that causes malaria, researchers found that two-thirds of those genes are essential for survival. This is the largest proportion of essential genes found in any organism studied to date, they said.
The scientists discovered that the parasite often disposes of genes that produce proteins that give its presence away to its host's immune system. This allows malaria to swiftly change its appearance to the human immune system and hence build up resistance to a vaccine, posing problems for the development of effective shots.
"Our study found that below the surface the parasite is more of a Formula 1 race car than a clunky people carrier: The parasite is fine-tuned and retains the absolute essential genes needed for growth," said Julian Rayner, who co-led this study at Britain's Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
Good and bad
He said this discovery, published Thursday in the journal Cell, had both positive and negative implications.
"The bad news is it can easily get rid of the genes behind the targets we are trying to design vaccines for, but the flip side is there are many more essential gene targets for new drugs than we previously thought," he said.
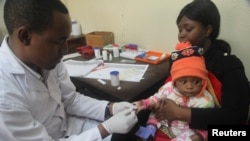
Malaria kills about half a million people a year, the vast majority of them children and babies in the poorest parts of sub-Saharan Africa. Beyond that, almost half the world's population is at risk of becoming infected with malaria, and more than 200 million people fall sick with it each year, according to World Health Organization figures.
Despite decades of scientific endeavor, the genetics of Plasmodium parasites have proved tricky to decipher.
This is partly because they are ancient organisms and about half their genes have no similar genes — homologs — in any other organism, Rayner's team explained, making it difficult for scientists to find clues to their function.
Francisco Javier Gamo, a malaria expert at GlaxoSmithKline, a British drugmaker active in this field of research, said the highest achievement for malaria scientists would be to discover genes that are essential across all of the parasite life cycle stages.
"If we could target those with drugs, it would leave malaria with nowhere to hide," he said.