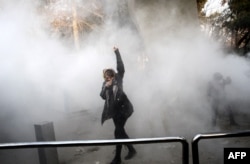The Iranian town of Doroud should be a prosperous place — nestled in a valley at the junction of two rivers in the Zagros Mountains, it’s in an area rich in metals to be mined and stone to be quarried. Last year, a military factory on the outskirts of town unveiled production of an advanced model of tanks.
Yet local officials have been pleading for months for the government to rescue its stagnant economy. Unemployment is around 30 percent, far above the official national rate of more than 12 percent. Young people graduate and find no work. The local steel and cement factories stopped production long ago, and their workers haven’t been paid for months. The military factory’s employees are mainly outsiders who live on its grounds, separate from the local economy.
“Unemployment is on an upward path,” Majid Kiyanpour, the local parliament representative for the town of 170,000, told Iranian media in August. “Unfortunately, the state is not paying attention.”
It's the economy
That’s a major reason Doroud has been a front line in the protests that have flared across Iran. Several thousand residents have been shown in online videos marching down Doroud’s main street, shouting, “Death to the dictator!” At night, young men set fires outside the gates of the mayor’s office and hurl stones at banks.
Anger and frustration over the economy have been the main fuel for the eruption of protests that began Dec. 28.
President Hassan Rouhani, a relative moderate, had promised that lifting most international sanctions under Iran’s landmark 2015 nuclear deal with the West would revive Iran’s long-suffering economy. But while the end of sanctions did open up a new influx of cash from increased oil exports, little has trickled down to the wider population. At the same time, Rouhani has enforced austerity policies that hit households hard.
Demonstrations have broken out mainly in dozens of smaller cities and towns like Doroud, where unemployment has been most painful and where many in the working class feel ignored.
Fury at ruling class
The working classes have long been a base of support for Iran’s hard-liners. But protesters have turned their fury against the ruling clerics and the elite Revolutionary Guard, accusing them of monopolizing the economy and soaking up the country’s wealth.
Many protests have seen a startlingly overt rejection of Iran’s system of government by Islamic clerics.
“They make a man into god and a nation into beggars!” goes the cry heard in videos of several marches. “Clerics with capital, give us our money back!”
Food prices jump
The initial spark for the protests was a sudden jump in food prices. It is believed that hard-line opponents of Rouhani instigated the first demonstrations in the conservative city of Mashhad in eastern Iran, trying to direct public anger at the president. But as protests spread from town to town, the backlash turned against the entire ruling class.
Further stoking the anger was the budget for the coming year that Rouhani unveiled in mid-December, calling for significant cuts in cash payouts established by Rouhani’s predecessor as a form of direct welfare. Since he came to office in 2013, Rouhani has been paring them back. The budget also envisaged a new jump in fuel prices.
But amid the cutbacks, the budget revealed large increases in funding for religious foundations that are a key part of the clerical state-above-the-state, which receive hundreds of millions of dollars each year from the public coffers.
After the lifting of most sanctions in early 2016, the economy saw a major boost — 13.4 percent growth in the GDP in 2016, compared to a 1.3 percent contraction the year before, according to the World Bank. But almost all that growth was in the oil sector.
Growth outside the oil sector was at 3.3 percent. Major foreign investment has failed to materialize, in part because of continued U.S. sanctions hampering access to international banking and the fear other sanctions could eventually return.
Iran’s official unemployment rate is at 12.4 percent, and unemployment among the young, those 19 to 29, has reached 28.8 percent, according to the government-run Statistical Center of Iran.
The provinces face more economic hardship, but the pain has been felt in the capital, Tehran, and other major cities as well. But there it’s been more cushioned within a large middle class. Many can ignore those picking through trash for food. However, in December 2016, Iranians expressed shock over a series of photographs in a local newspaper showing homeless drug addicts sleeping in open graves in Shahriar, on Tehran’s western outskirts.